NM500 Neuromorphic Classification of Leeds Butterfly
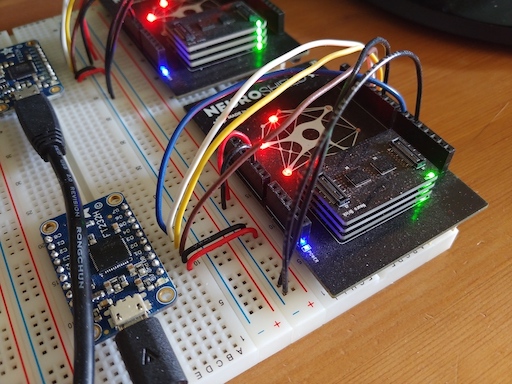
This Kaggle project extends a previous project to demonstrate an application of General Vision's NM500 neuromorphic chip to image classification. The chip implements a Restricted Coulomb Energy / Radial Basis Function network in hardware using 576 artificial neurons. A pattern of up to 256 bytes in length can be presented to the neurons in parallel, essentially realizing a constant-time classification relative to the network size. Furthermore, multiple NM500 chips can be modularly connected into arbitrarily large networks while continuing to incur essentially no increase in computation time. General Vision provides an evaluation board, the NeuroShield, which includes a single NM500 chip. The NeuroShield also accepts stackable NeuroBrick boards, each providing an additional two NM500 chips. For this application I used four NeuroShields, each maxed out with three NeuroBricks for at total of 4032 neurons per NeuroShield. The four NeuroShields were operated in parallel on four separate USB connections using an Adafruit FT232H chip (and board) to mediate the SPI interface between the computer and the NeuroShields. This parallel architecture achieved a 3.1X speedup in query access times over the rate achieved with a single NeuroShield. The Kaggle project classifies the Leeds Butterfly dataset with four NeuroShields, achieving a 93.4% classification accuracy. Please head over to Kaggle to read the details of this project. |